
Scabies
Which type of mite?
What is scabies?
Life cycle of the scabies mite
Symptoms of scabies
Treatment of scabies
Which type of mite?
Three different types of mites commonly infect humans:
- Demodex mites.
- Scabies mites, which are closely related to the mites which cause mange in dogs and other animals. Sometimes the mites from a dog, cat or bird can pass to humans and cause serious serious itching, rashes and lesions. Scabies mites live predominantly on animals but can also infect humans. They don't normally complete their life cycle in humans, but when they do they can make for intensely itchy nights.
- Bird mites, causing the sensation of crawling on the skin, especially at night. They are also virtually impossible to get rid of without eliminating their source (the bird's nest).
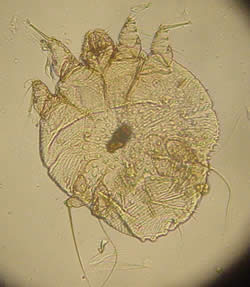
It is very important to identify which type of mite you have, because their treatments are different. Incorrect treatment will result in ongoing infection.
What is scabies?
The scabies mite (sarcoptes scabiei or itch mite) is a parasitic arthropod that burrows into skin and causes intense, itchy skin rashes. The scabies mite affects humans and other primates. In animals such as dogs, cats, pigs, cows and other bovids, wombats and koalas a different but related mite species causes sarcoptic mange.
Mites are usually spread by skin to skin contact. Contact must be prolonged (a quick handshake or hug is usually safe!) and often comes from an infected sexual or sleeping partner, or family member. Mites can live as long as 2-3 days in clothing or bedding, making it possible to catch scabies from people who share the same infected bed, linen or towels. Scabies mites die when exposed to a temperature of 50C / 122F for 10 minutes. Scabies spreads more easily in crowded conditions where an infected person is in close contact with others, such as aged care centres or child day care.
It is not possible to get the human scabies mites from a pet with mange. If you are infected with animal mites from a pet you may suffer intense itching for a up to ten days before they die off.
About 2% of the British population are infected with scabies mites.
Life cycle of the scabies mite
Scabies mites have a life of about 1-3 months. They start as eggs that are laid under the skin. The larvae hatch after 3-5 days and climb up to the surface of the skin. They then burrow down into hair follicles and make pouches they will use for moulting. They moult several times, turning into lymphs, and finally to adult mites. The males take 9-11 days, and the females 17 days. The mites then mate just once, which leaves the female fertile for the rest of her life (1-2 months). The impregnated female then leaves the moulting pouch to find a new place on the skin for a permanent burrow. She burrows down into the skin, and lays two to three eggs a day until she dies.
Adult scabies mites have a convex tortoise-like body. Females are 0.3-0.45 mm (0.012-0.018") long, which would make her just visible if you dug one out. The males are just over half that size, and you need a microscope to see them.
Symptoms of scabies
After the first infection with mites, it takes about 2-6 weeks for symptoms to appear (for people never previously exposed to scabies). In a few cases, symptoms have taken months or years to appear. For those having been previously exposed, the symptoms can appear within one or several days after infestation.
- Itching. The action of the mites burrowing under the skin produces an intense itch. When they lay eggs, the skin has an allergic response that again, produces more itching. In humans, as few as a dozen mites can cause agonising itching, especially at night or after a hot bath. Scratching can further damage the skin and introduce infective bacteria, which may lead to impetigo or eczema. The itching is intensified by warmth.
- In humans, scabies is most commonly found around the hands or wrists, but the mites can also be found on other parts of the body such as feet, elbows, back, buttocks and external genitals. They are seldom found on the face or scalp, except in people with a suppressed immune system. The mites prefer to live in crevices of the body, such as on the webs of fingers and toes, around the genital area, and under the breasts of women. A mite infection on the face or scalp may be demodex mites rather than scabies.
- Several mosquito-like bites may appear on the skin. The area may be red, and sometimes S-shaped burrow tracks or lines may be visible.
- In infants blisters and pustules on the palms and soles of the feet are a characteristic symptom.
- In the elderly and those with an impaired immune system, the mites can proliferate and cause widespread thick crusting on the hands, arms and other parts of the body (except the face).
Treatment of scabies
Before starting treatment, sexual partners and all those in close contact should be examined. Scabies is highly contagious and it is easy to get re-infested. The other members of a household should also be treated for scabies even if they have no symptoms.
Clothing, sheets and towels should be washed in hot water. Pillows, blankets, stuffed toys and other items that cannot be washed should be isolated for a minimum of three days. Each room in the house should be vacuumed, including furniture, cushions, etc (mites can survive for up to 3 days away from the body). Also think about car seats and any other places that may have contact with bare or infected skin.
After the parasites have been eradicated, there is often a significant delay before the symptoms go. This is because dead mites are still under the skin, and it takes time for them to work their way to the surface as the skin repairs and sloughs off. In addition, the mites caused an allergic reaction that needs to resolve.
If you are re-infected at this time, symptoms can start again in as little as 24 hours.
